How to Manage Risk Points
About 728 wordsAbout 2 min
I. Function Introduction
Risk points refer to facilities, locations, sites, and areas accompanied by risks, as well as operational activities carrying risks conducted at these facilities, locations, sites, and areas, or a combination of both.
Through Risk Control Guard, establish a risk point management database to achieve full lifecycle management of risk points, including registration, classification, risk level assessment, responsibility assignment, control measure formulation and tracking, etc.
Access Entry:
- Administrator logs in to management backend
- Navigation menu select: 【Risk Identification】→【Risk Points】
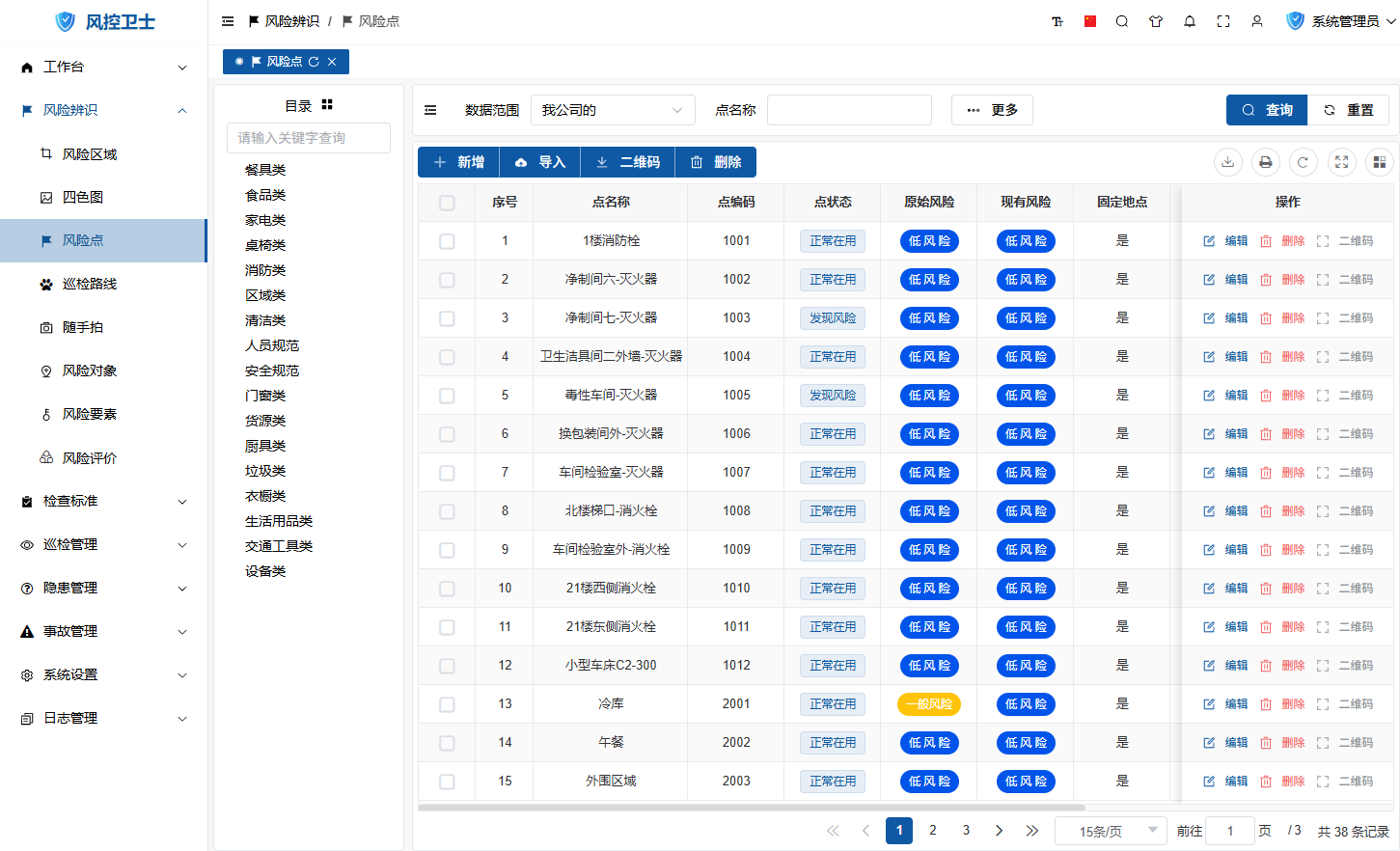
II. Core Operation Guide
1. Add New Risk Point
Operation Steps:
- Click "New" button on toolbar
- Fill in key information:
- Basic Information: Name, location, type
- Risk Attributes: Risk level, risk type
- Control Measures: Technical/management/emergency measures
- Responsibility Assignment: Responsible department, responsible person
- Click "Save" to complete creation
Detailed operation: Add Risk Point Guide
2. Batch Import
Operation Steps:
- Click "Import" button on toolbar
- Download Excel template
- Fill data according to specifications
- Upload file and verify
Detailed operation: Batch Import Guide
3. QR Code Management
Operation Steps:
- Locate target risk point
- Click "QR Code" button in operation column
- Select operation:
- Direct print (A4/label paper)
- Export PDF (vector image)
Detailed operation: QR Code Signage Guide
4. Modify Risk Point
Operation Steps:
- Locate target risk point
- Click "Edit" button in operation column
- Modify information:
- Basic information
- Risk attributes
- Control measures
- Click "Save" to submit
5. Delete Risk Point
Operation Steps:
- Locate target risk point
- Click "Delete" button in operation column
- Confirm deletion
Precautions:
- Risk points with associated data cannot be deleted
- Historical records are retained for 90 days after deletion
III. Category Directory Management
1. Directory Operation Guide
| Operation | Steps | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| Add Top-level Directory | 1. Hover mouse over "Directory" text 2. Click "Add Directory" 3. Enter name and click blank area | |
| Add Subdirectory | 1. Right-click target directory 2. Select "Add" 3. Enter name and click blank area | |
| Rename Directory | 1. Right-click target directory 2. Select "Modify" 3. Enter new name and click blank area | |
| Delete Directory | 1. Right-click target directory 2. Select "Delete" 3. Confirm operation | |
| Adjust Order | Drag directory to target position |
IV. Status Management
1. Status Types and Transitions
| Status | Trigger Condition | System Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Operation | Initial state/rectification completed | Generate inspection tasks |
| Risk Identified | Inspection result unqualified | Trigger hazard reporting process |
| Hazard Rectification | Associated with hazard management ticket | Suspend inspection tasks |
| Out of Service | Manually set/equipment scrapped | Stop all tasks |
2. Status Change Rules
- Automatic transition: Unqualified inspection → Risk Identified
- Manual setting: Out of Service requires administrator operation
- Closed-loop requirement: Hazard rectification requires associated work order
V. Risk Level Management
1. Risk Classification Standard
| Level | Color | Control Level | Inspection Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Major Risk | Red | Company level | Daily |
| High Risk | Orange | Department level | Weekly |
| Medium Risk | Yellow | Workshop level | Biweekly |
| Low Risk | Blue | Team level | Monthly |
2. Risk Type Explanation
- Inherent Risk:
- Initial risk without considering control measures
- Directly determined by risk administrator
- Example: Flammable material risk in tank area
- Residual Risk:
- Remaining risk under existing control measures
- Dynamically evaluated through assessment process
- Changes dynamically with hazard management
Graded Control Principles
- Major Risk: Direct control by company safety committee
- High Risk: Main responsibility of department head
- Medium Risk: Responsibility of workshop director
- Low Risk: Daily monitoring by team leader
VI. Implementation Recommendations
1. Risk Point Investigation Standards
- Comprehensive Coverage:
- Production equipment and facilities
- Operational activity areas
- Auxiliary facilities (power distribution/fire protection)
- Plant public areas
- Information Elements:
- Unique code
- GPS positioning
- Risk photos
- Potential accident types
2. List Establishment Standards
- Equipment and Facilities List:
- Organized by functional zones (production/storage/loading)
- Include equipment technical parameters
- Attach equipment schematic diagrams
- Operational Activities List:
- Cover routine/non-routine operations
- Highlight high-risk operations:
- Hot work
- Confined space entry
- Large equipment maintenance
- Clarify operational procedures
3. Dynamic Management Mechanism
- Regular Assessment:
- Major Risk: Quarterly assessment
- High Risk: Semi-annual assessment
- Routine Risk: Annual assessment
- Change Management:
- Update within 72 hours after equipment modification
- Synchronize risk point updates with process changes
- Complete registration before new project commissioning
- Digital Dashboard:
- Risk distribution heatmap
- Real-time status monitoring
- Automatic warning alerts
