accident
About 563 wordsAbout 2 min
I. Function Introduction
Accident management is the core of enterprise safety management, achieving through systematic recording, analysis and prevention of accidents:
- Accident Recording: Complete documentation of accident details
- Root Cause Analysis: In-depth investigation of accident origins
- Preventive Control: Develop targeted prevention measures
- Compliance Management: Meet regulatory reporting requirements
Core Value:
- Prevent accident recurrence
- Improve safety management level
- Protect personnel safety
- Reduce enterprise economic losses
Access Entry:
- Administrator logs into management backend
- Navigation menu: 【Accident Management】→【Accident Archives】
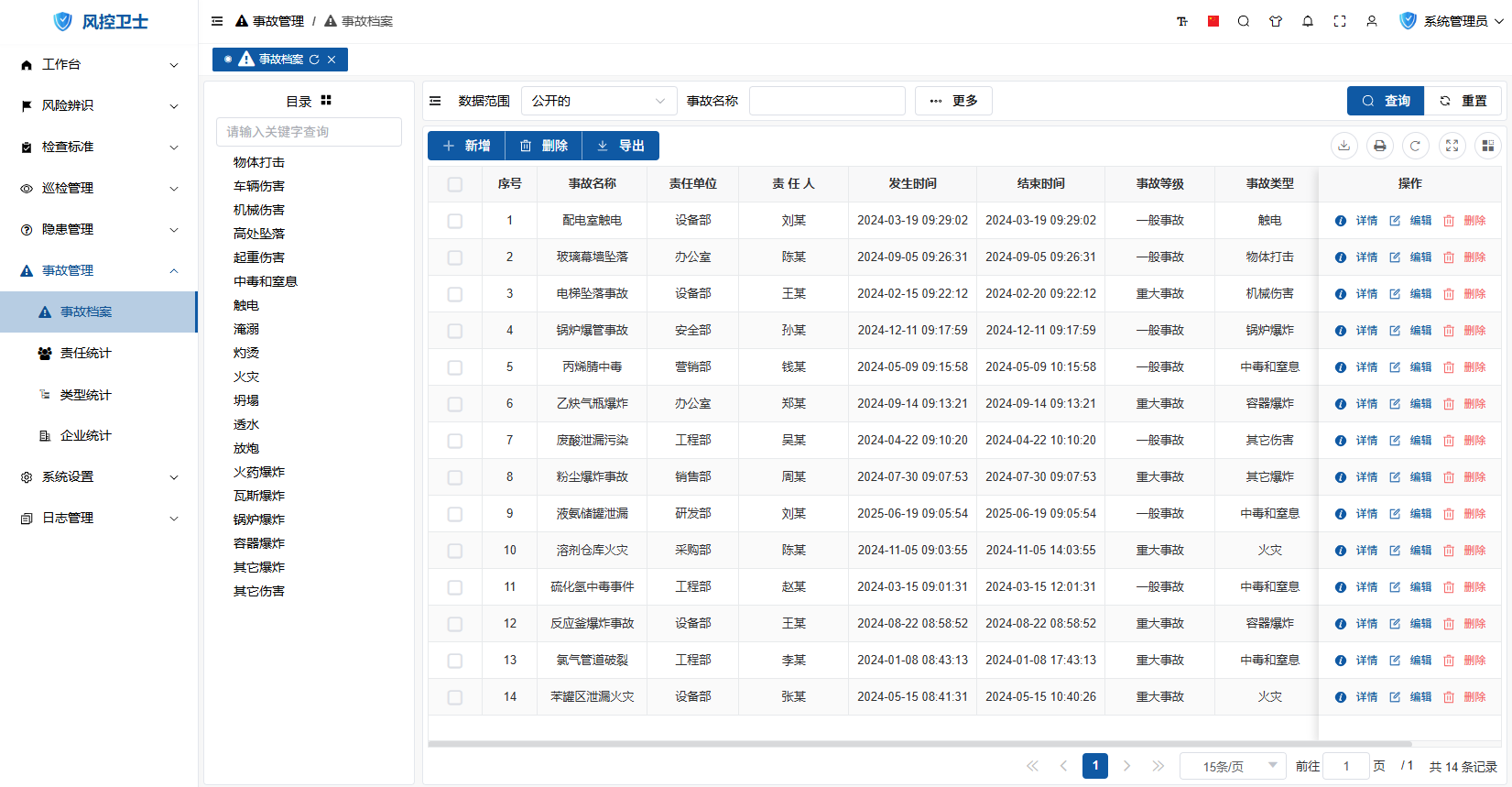
II. Accident Archives Management
1. Add Accident Archive
Operation Steps:
- Click "New" button on toolbar
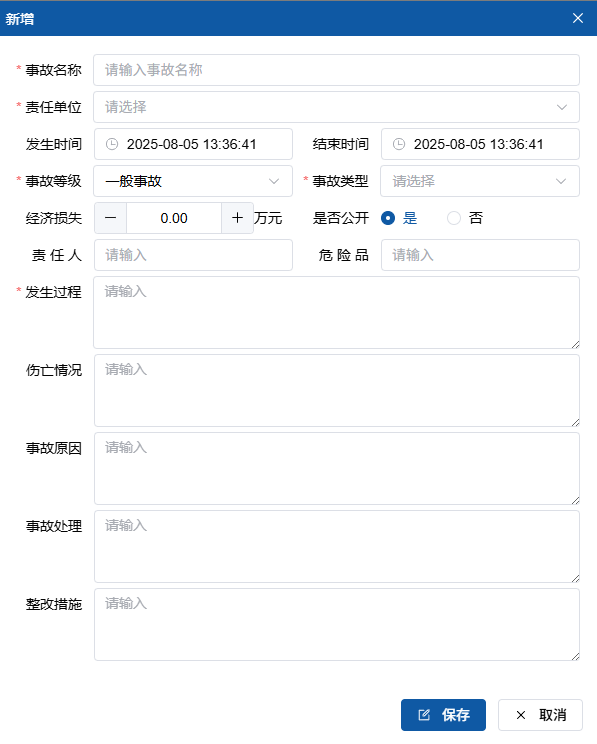
- Fill key information:
- Basic Information:
- Accident Name (e.g. "Workshop A Machinery Injury")
- Responsible Unit (Department accountable)
- Responsible Person (Accountable individual)
- Hazardous Materials (Items causing accident)
- Occurrence Time (Exact to minute)
- End Time (Exact to minute)
- Accident Details:
- Accident Type (According to GB6441 classification)
- Severity Level (Major/General)
- Casualty Status (Fatalities/Severe/Minor injuries)
- Economic Loss (Direct/Indirect losses)
- Occurrence Process (Detailed description)
- Causes
- Handling Measures
- Corrective Actions
- Basic Information:
- Click "Save" to complete registration
2. Modify Accident Archive
Operation Steps:
- Locate target accident
- Click
edit button in operation column
- Modify:
- Accident details
- Basic information
- Analysis conclusions
- Click "Save" to submit
3. Delete Accident Archive
Operation Steps:
- Locate target accident
- Click
delete button in operation column
- Confirm deletion operation
III. Category Directory Management
Operation Guide
| Operation | Steps | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| Add Top-level Directory | 1. Hover over "Directory" text 2. Click "Add Directory" 3. Enter name and click blank area | |
| Add Subdirectory | 1. Right-click target directory 2. Select "Add" 3. Enter name and click blank area | |
| Rename Directory | 1. Right-click target directory 2. Select "Modify" 3. Enter new name and click blank area | |
| Delete Directory | 1. Right-click target directory 2. Select "Delete" 3. Confirm operation | |
| Adjust Order | Drag directory to target position |
Management Standards
- Directory Structure:
- Top-level: By accident type (Mechanical/Electrical/Fire etc.)
- Naming Rules:
- Concise and clear (≤6 characters)
- Comply with GB6441 standard
IV. Accident Investigation Process
- Accident Reporting: Immediate reporting of accident
- Scene Protection: Secure site and preserve evidence
- Preliminary Investigation: Collect basic information
- Cause Analysis: Identify direct/indirect causes
- Responsibility Determination: Identify accountable parties
- Corrective Actions: Develop prevention plan
- Report Preparation: Form investigation report
- Case Closure: Complete accident handling
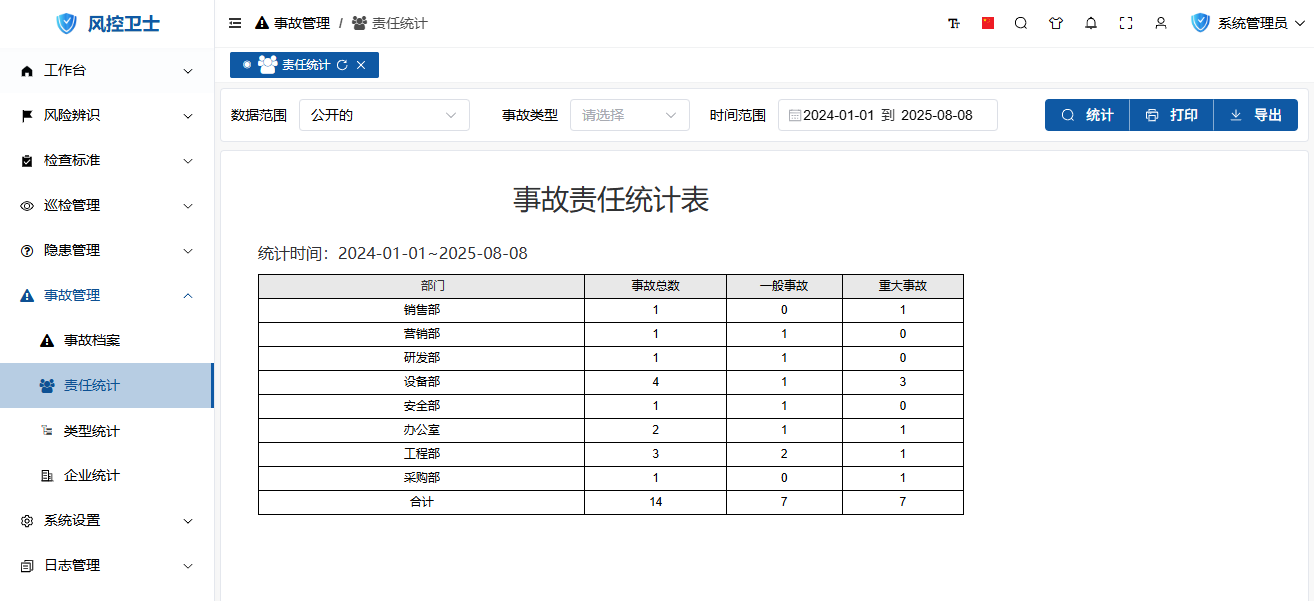
V. Statistical Analysis
1. Responsibility Statistics
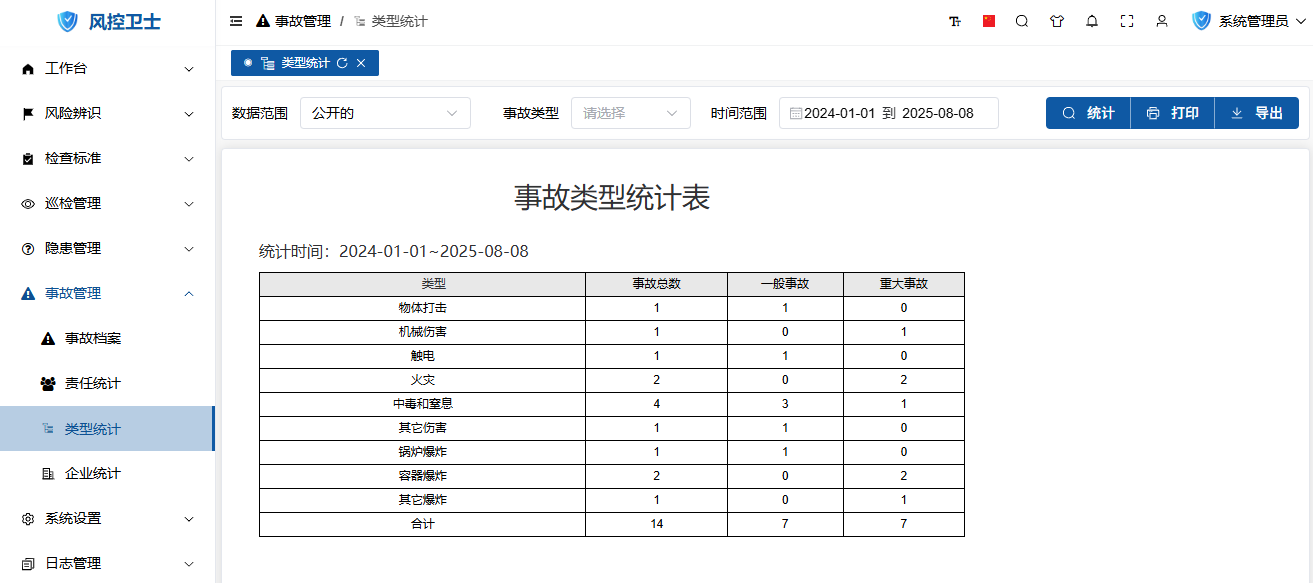
2. Type Statistics
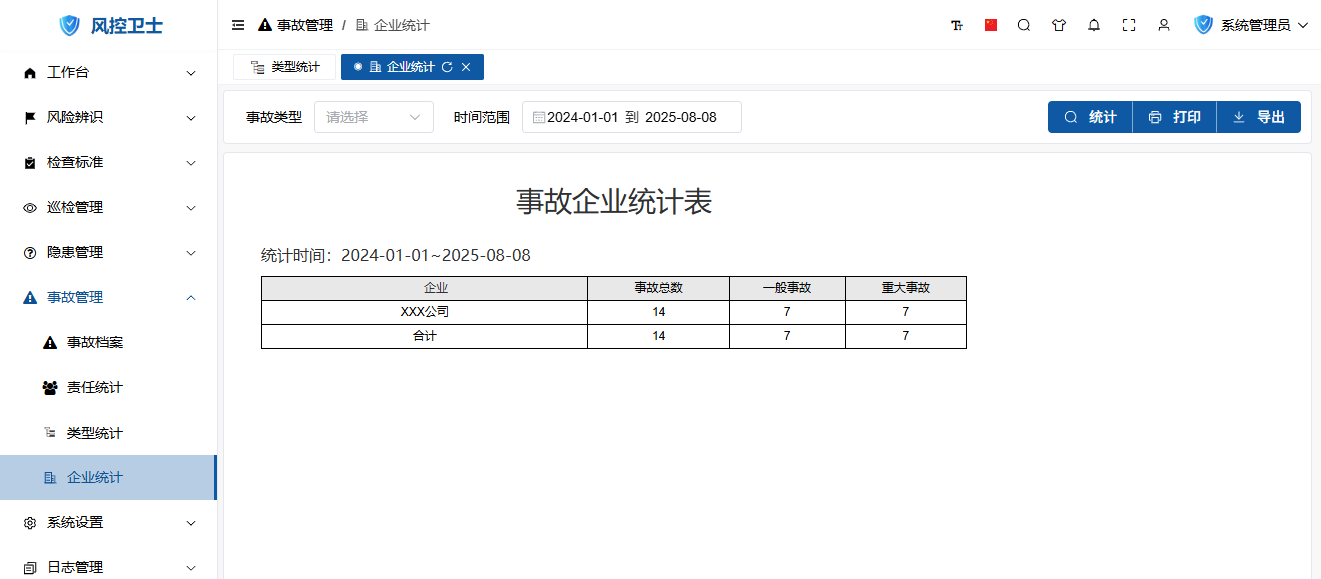
3. Enterprise Statistics
VI. Best Practices
1. Management Strategies
- Four No's Principle:
- No closure without identifying causes
- No closure without handling responsible persons
- No closure without implementing corrective actions
- No closure without educating relevant personnel
- Prevention Mechanisms:
- Establish accident warning indicators
- Implement Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Conduct safety warning education
- Emergency Management:
- Improve emergency plans
- Regularly organize drills
- Establish rapid response mechanisms
2. Technical Applications
- Digital Forensics:
- 3D scene reconstruction
- Video intelligent analysis
- Electronic data recovery
- Big Data Analysis:
- Accident pattern recognition
- Risk prediction models
- Safety performance evaluation
VII. Precautions
- Reporting Timelines:
- General accidents: Report within 24 hours
- Major accidents: Report immediately
- Archive Management:
- Retention period ≥30 years
- Electronic + paper dual backup
- Information Confidentiality:
- Encrypt sensitive information
- Control access scope
